NA:Blockchain Flow
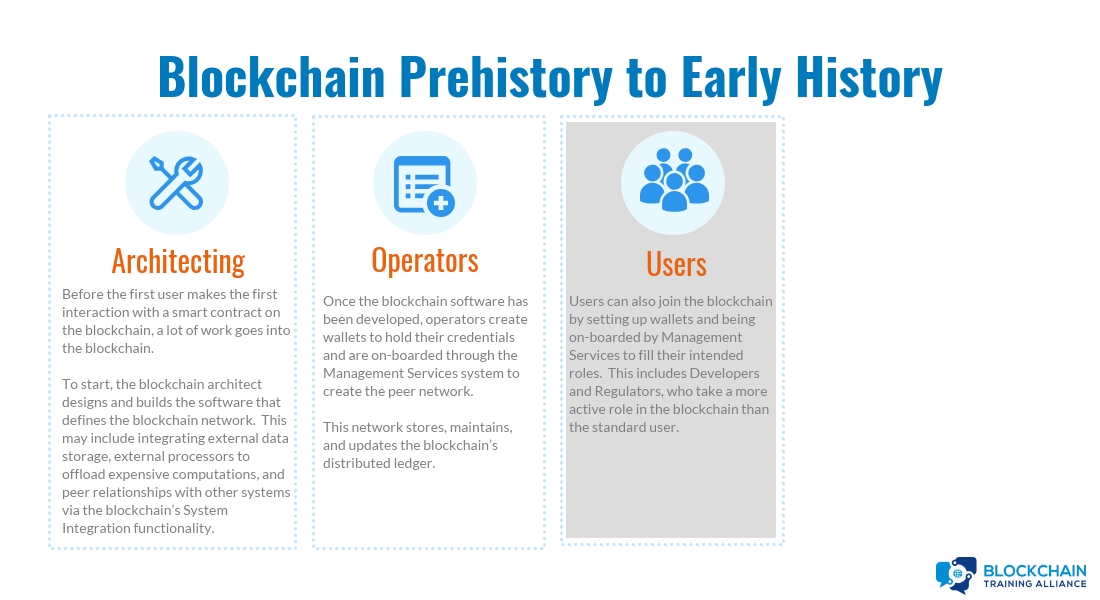
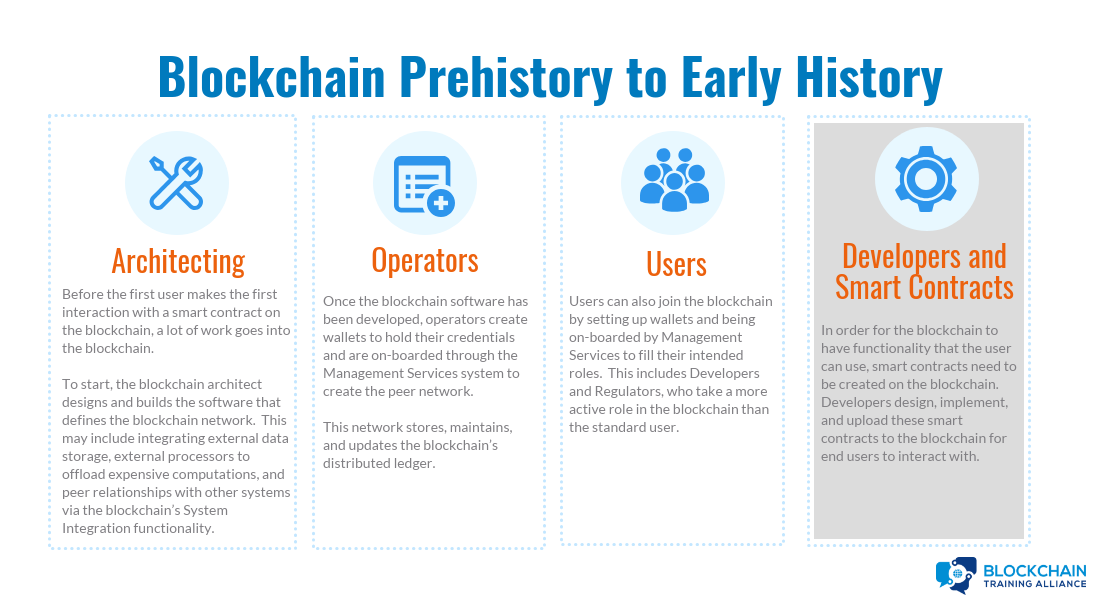
Blockchain Prehistory to Early History: Architecting
 Blockchain architect designs and builds blockchain network:
Blockchain architect designs and builds blockchain network:
- Optionally, traditional databases are set up to store data off-chain.
- Optionally, external processors are set up to allow blockchain to offload computation if necessary.
- Optionally, peer relationships are set up with external systems via system integration.
Blockchain Prehistory to Early History: Operators

Blockchain Prehistory to Early History: Users
Blockchain Prehistory to Early History: Developers and Smart Contracts
Video: Blockchain Transaction Flow
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Operation or Transaction Performed
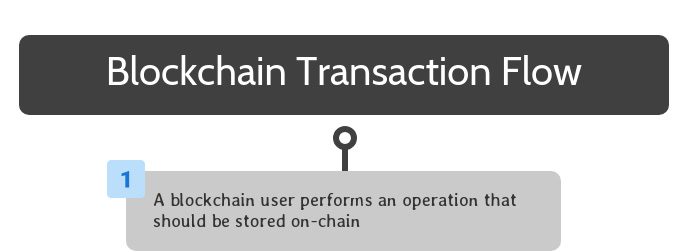
Once a blockchain solution is completely set up, end users can interact with its smart contracts to take advantage of its available functionality.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Smart Contract Triggered
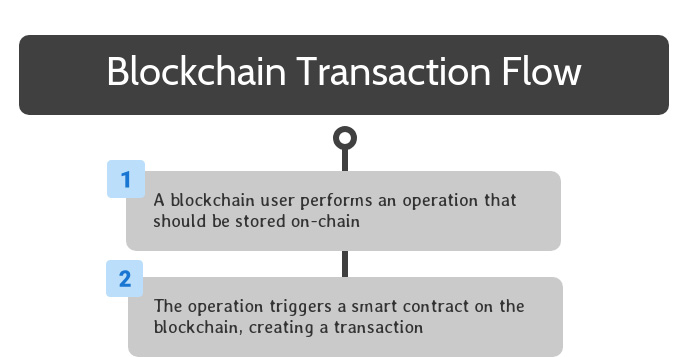
To begin, a blockchain user performs an operation that should be stored on the blockchain. This can be accomplished by interacting with software that interfaces with a smart contract on the blockchain.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Operators Spread Transaction
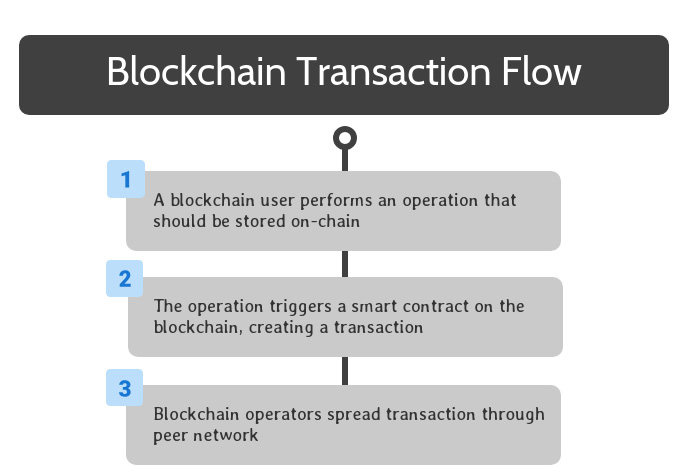
Once the smart contract is triggered, the relevant code is encapsulated in a transaction, which spreads to all blockchain operators through peer-to-peer transactions on their network.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Collections of Previous and Creation of New
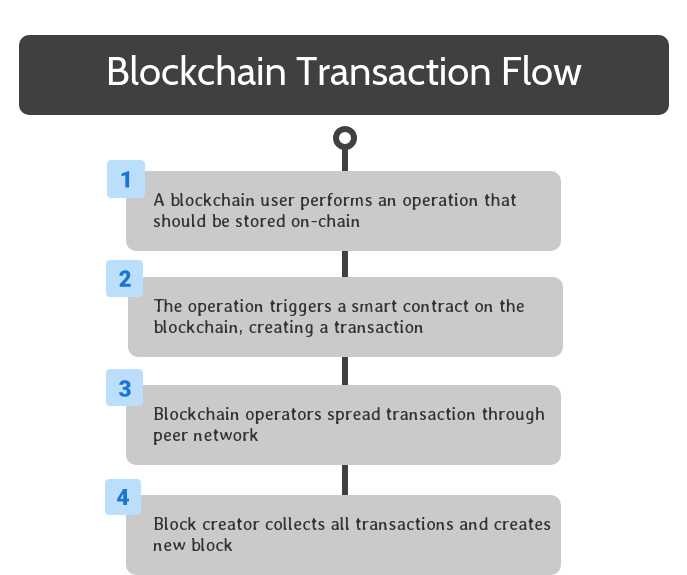
Through the blockchain’s consensus mechanism, one of the blockchain operators is selected to be the creator of the next block on the blockchain. This operator collects all of the transactions created since the previous block into a new block, and finalizes the new block.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Spread New Block
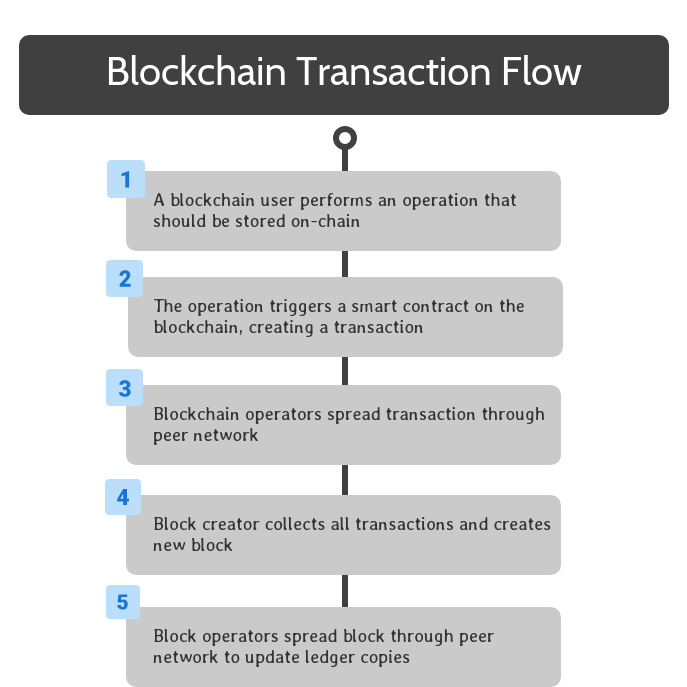
This block is spread throughout the peer network through the same peer-to-peer communications as transactions.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Execute Code
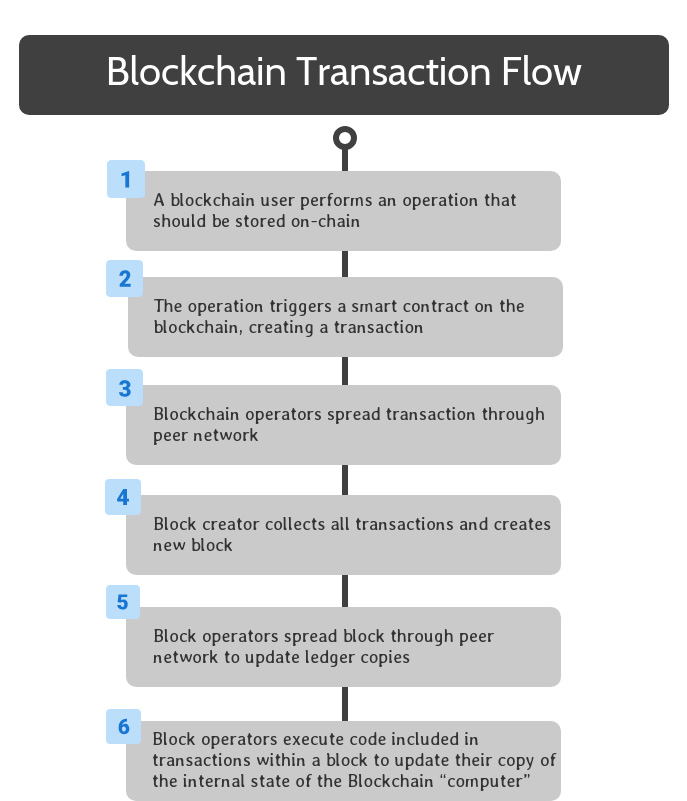
When block operators receive a copy of the new block, they add it to their copy of the distributed ledger and execute the smart contract code included in each transaction in the block. This guarantees that all members of the peer network agree on the current state of the blockchain’s distributed computer.
Blockchain Transaction Flow: Operation Complete
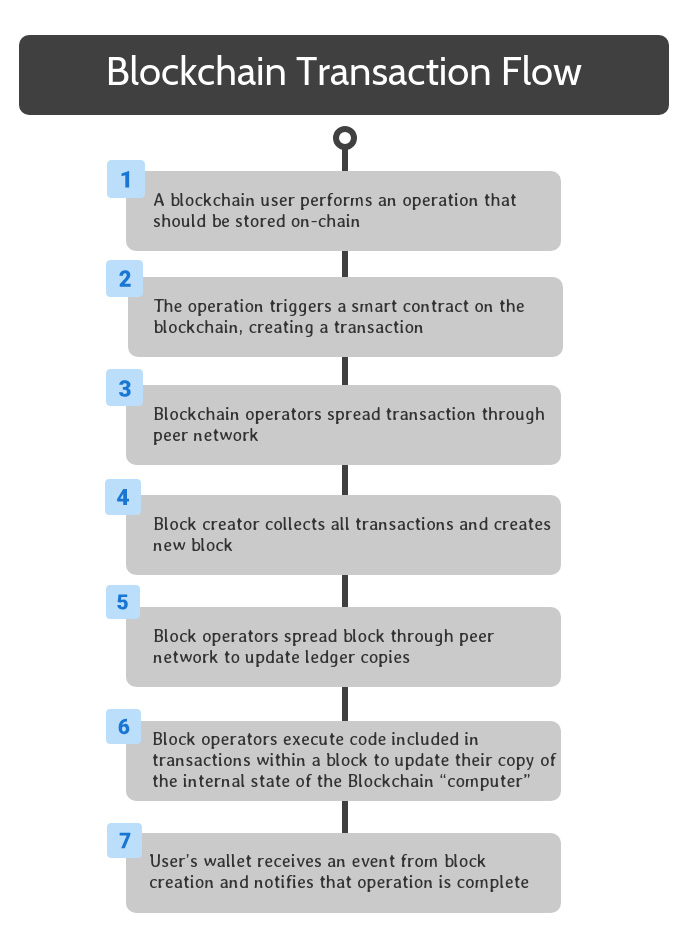
The user’s wallet monitors for the creation of new blocks that include transactions associated with the user. When a block containing the completed code from the user’s operation is received, an event is created to notify the user that the operation is complete.