NA:Public and Permissioned Blockchains
Understanding the Difference
When we try to understand the main difference between a public and private blockchain, it is important to appreciate that the terminology in the media gets routinely improperly stated.
If you have some time and would like a much deeper dive into public blockchain vs. private blockchain for the enterprise, there is a great webinar on this topic: "Public Blockchain vs Private Blockchain for the Enterprise".
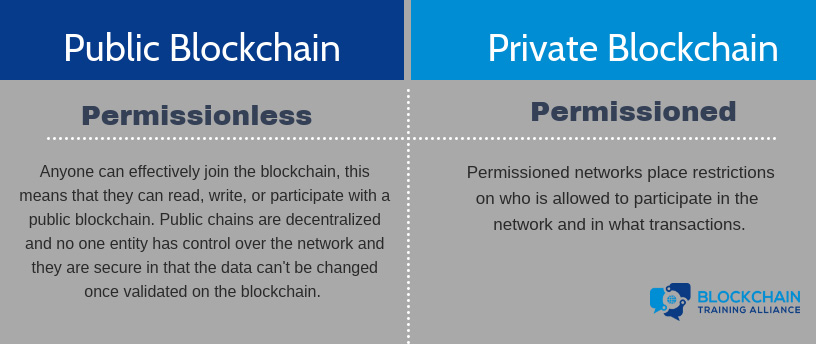
A public blockchain is really a permissionless blockchain. Anyone can effectively join the blockchain, meaning that they can read, write, or participate with a public blockchain. Public chains are decentralized, no one entity has control over the network, and they are secure in that the data can't be changed once validated on the blockchain.
A private blockchain is really a permissioned blockchain. Permissioned networks place restrictions on who is allowed to participate in the network and in what transactions.
=======================================================
Video: Public (Permissionless) Blockchains
Public Blockchain Benefits
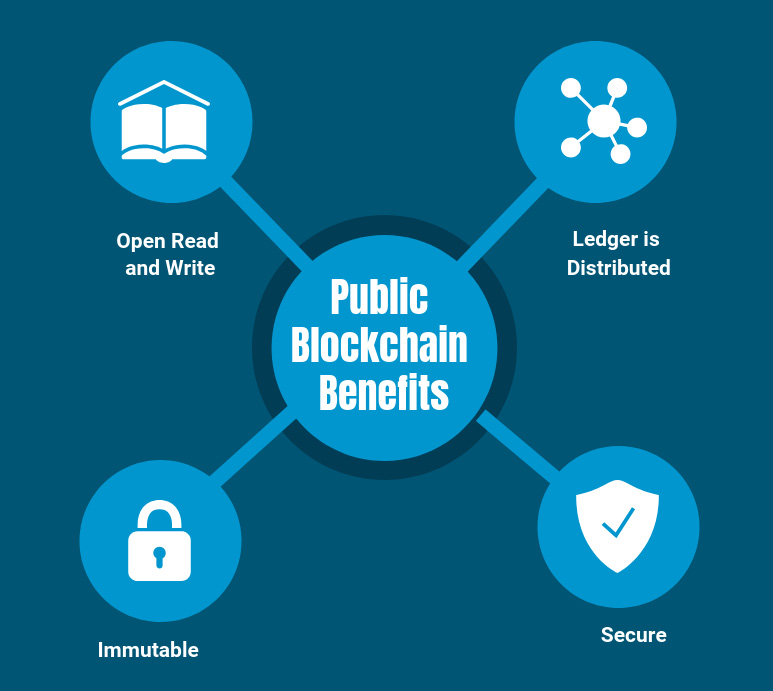
The benefits of public blockchain are:
- Open Read and Write
Anyone can participate by submitting transactions to the blockchain, such as Ethereum or Bitcoin; transactions can be viewed on the blockchain explorer. - Ledger Is Distributed
The database is not centralized like in a client- server approach, and all nodes in the blockchain participate in the transaction validation. - Immutable
When something is written to the blockchain, it can not be changed. - Secure Due to Mining (51% rule)
For example, with Bitcoin, obtaining a majority of network power could potentially enable massive double spending, and the ability to prevent transaction confirmations, among other potentially nefarious acts.
Video: Private (Permissioned) Blockchains
Private (Permissioned) Blockchains
Lets discuss what private blockchains are and why they are utilized by enterprises:
- Private blockchains are also referred to as permissioned or enterprise blockchains. Enterprises need to ensure some level of security, privacy, compliance, performance, and many of the properties that a private blockchain can provide.
- Can be open sourced, consortium, or privately developed. There are many options for a private blockchain, and the most common ones are R3 Corda, Hyperledger, and Quorum.
- Transactions are processed by select nodes in the blockchain. From a performance perspective, this is where having only a few nodes process transactions vs. 14,000 nodes in Ethereum’s case can really create a performance gain around latency and transaction speed.
- Transactions are not publicly viewable (transparent) in the blockchain, and only select nodes can access the ledger.
- Locally distributed, examples include: R3 Corda can transact between nodes, and the rest of the blockchain does not participate.
Private (Permissioned) Blockchain Benefits
The benefits of private blockchain are:
- Enterprise Permissioned
The enterprise controls the resources and access to the blockchain, hence private and/or permissioned. - Faster Transactions
When you distribute the nodes locally, but also have much less nodes to participate in the ledger, the performance is faster. - Better Scalability
Being able to add nodes and services on demand can provide a great advantage to the enterprise. - Compliance Support
As an enterprise, you likely would have compliance requirements to adhere to, and having control of your infrastructure would enable this requirement more seamlessly. - Consensus More Efficient (less nodes)
Enterprise or private blockchains have less nodes and usually have a different consensus algorithm, such as BFT vs. POW.
Video: Public and Private Comparison
Public and Private Blockchain Decisions
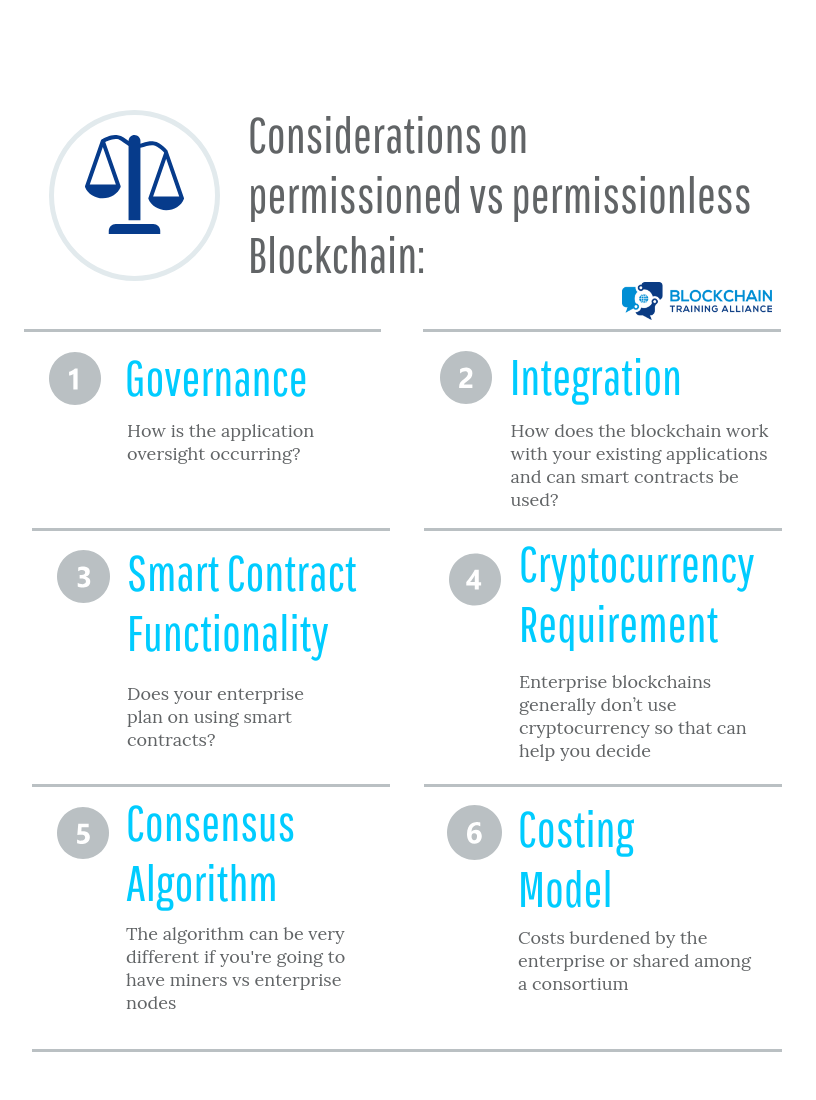
When it comes to decision making around what blockchain model to use, it's important to understand the considerations: